Children are very exposed to anemia. In this text you can find information about signs of anemia in children.
Anemia is a very significant health problem around the world, especially in children`s age. In 2011. WHO published that approximately 300 million children globally had anemia. Anemia is a condition in which the amount of red blood cells or their oxygen-carrying capacity is insufficient to meet physiologic needs. It can happen because our body is destroying red blood cells, or losing too many red blood cells (due to excessive bleeding from an injury or surgery), or producing red blood cells too.
The most common cause of anemia in children appears to be the deficiency in iron, which is an essential nutrient for both cell growth and the development in the neural and immune systems. Iron deficiency can originate from inadequate intake or absorption of dietary iron, blood loss or increased need during the growth period. Iron deficiency anemia is the most common in children due to their increased iron requirements in the periods of rapid growth, the first year of life and adolescence are the two groups of children especially disposed to anemia. As a result, a child with iron deficiency may have learning and behavioral problems.
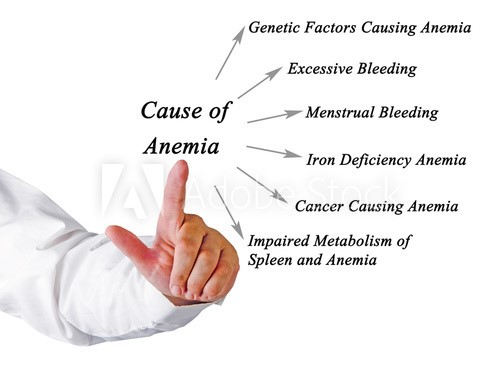
Except for iron deficiency anemia there are many more types of anemia, but in children`s age some of the most common are:
- Megaloblastic anemia (Deficiency in vitamin B₁₂, which is important in the making of red blood cells, or deficiency in folic acid)
- Aplastic anemia (When the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells, due to a viral infection, or exposure to certain toxins, or some genetic and chronic diseases)
- Hemolytic anemia (Our body destroys red blood cells faster than they can be replaced)
-Sickle cell anemia is a type of hemolytic anemia, it`s an inherited type of anemia with an abnormal shape of red blood cells
What are common signs of anemia in children?
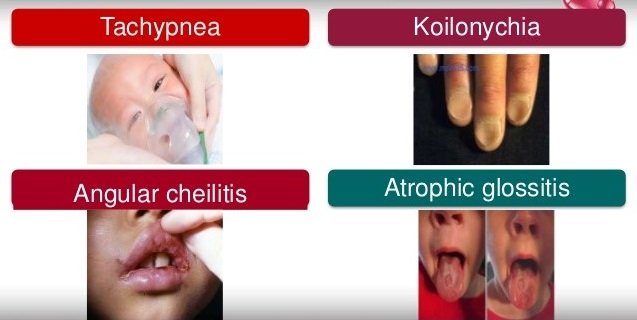
Most of the signs of
After this early first symptoms, other common signs show up, which include:
- Irritability
- Being tired very easily, also lack of energy
- Dizziness, or vertigo
- Headache
- Lightheadedness
- Irregular menstrual cycle (in adolescent girls)
- Mild weakness
- Sore or swollen tongue
- Low appetite
Children with severe anemia may have some of the additional signs and symptoms:
- Fast heartbeat, due to this rapid heart rate
- Shortness of breath or trouble catching a breath
- Swollen hands and feet
- Slow or delayed growth and development
- Poor wound and tissue healing
Iron-deficiency anemia symptoms in children:
This type of anemia develops over time. Firstly, the amount of iron in the body rapidly goes down and the child starts to have iron-deficiency. In this stadium muscle and brain function are endangered. At this point, the red blood cells don’t change much, because the body uses most of its iron to make hemoglobin. In time, all the iron gets used up, and the body starts making fewer red blood cells, this is the point where the body becomes anemic.
At this point, symptoms and signs may be:
- Tiredness or weakness
- Pale skin, especially around the hands, nail beds and eyelids
- Rapid heartbeat or a heart murmur
- Irritability
- Low appetite
- Dizziness or feeling lightheaded
Other signs of anemia in children
In rare cases, a child with this type of anemia may develop “pica” (pronounced pie-
In infants and preschoolers, this type of anemia can cause behavioral disturbances or developmental delays. Behavioral disturbances can manifest like decreased motor activity, problems with paying attention, or problems with social interaction. If chronic iron deficiency anemia is not treated in long-term it can result in permanent impairment of development.
Anemia due to excessive destruction of red blood cells in children can cause jaundice (yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mouth), an enlarged spleen or liver, and dark tea-colored urine.
The signs of anemia in children may sometimes look more like other health conditions or blood problems. Anemia is often a symptom of another disease.
Even non-severe anemia can affect a child`s focus, energy and ability to learn. So it is very important to take your child to the doctor as soon as you notice any of these signs or symptoms.
